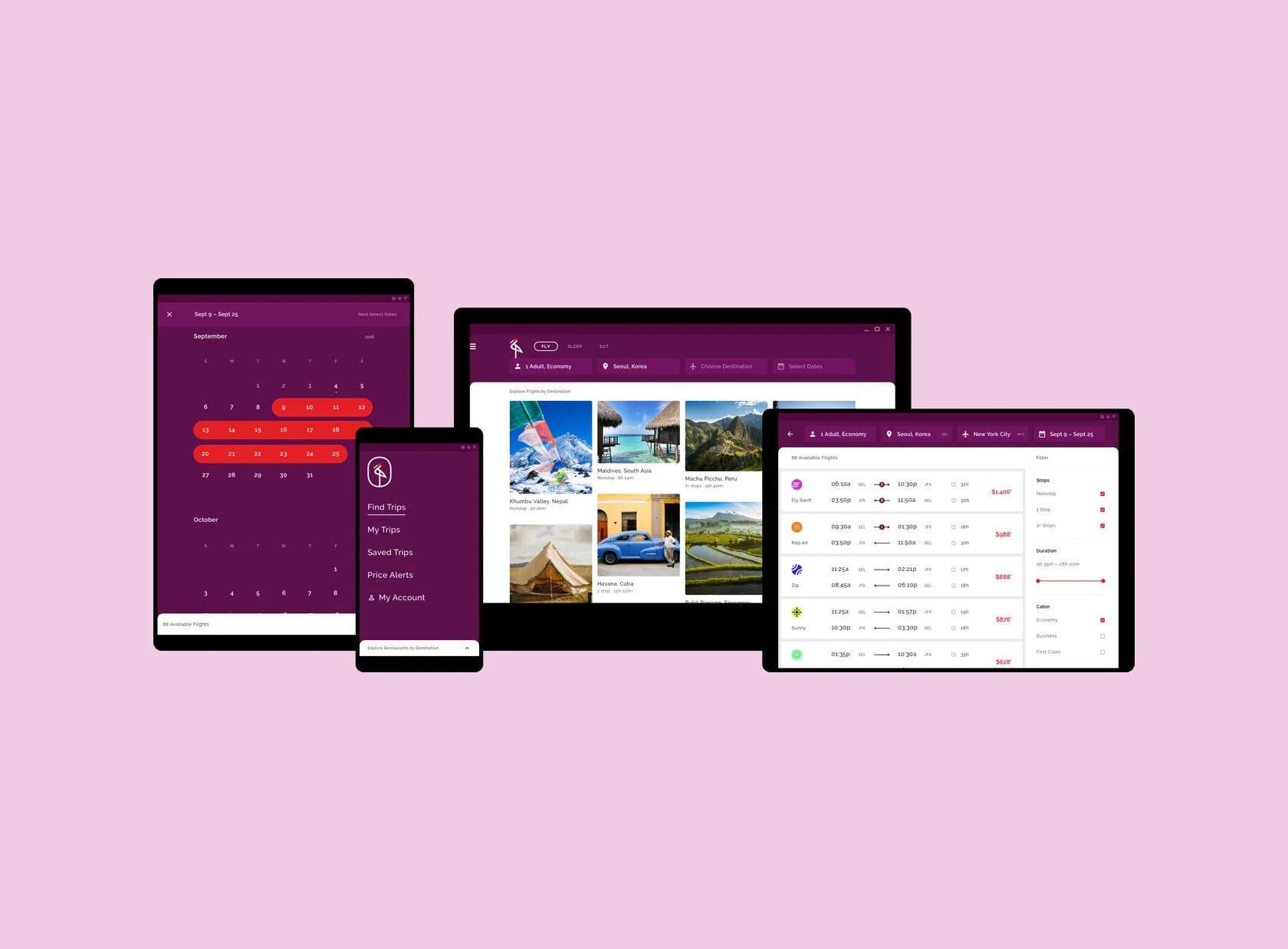
Material design is the newest design trend in the realm of web and app design. This new mobile-first design language was introduced by Google in 2014, offering an improved way of creating beautiful apps and websites that would work on any device.
What is Material Design?
Material Design is a standard for building software that combines classic principles of good design with innovative technology and thoughtful consideration of how people interact with devices. Google’s goal is to support material design across all platforms and apps, ensuring a consistent experience on every type of Android device.
This web design trend was developed by the Google team in 2014 with lots of unknown details which are typical for google services. The main reason to develop it was to make website interfaces similar across all platforms, not only on PCs but also on tablets and smartphones. As you know, the Android system was developed by that corporation too, so this development has been especially useful for them.
It is a visual language as its official user interface (UI) design concept. Google’s goal was to create a unified system that allows for a seamless experience across all platforms. In addition, the designers focused on creating efficient solutions to common problems with Android app development. As mentioned before, its key features are: being material – it uses surfaces and shadows to create depth; responsive – it works across many different devices; animation – provides meaning about what users can do next or how they can navigate through the app; consistent attributions for every platform.
What makes this web design so attractive?
Today there are so many web design trends starting with flat design and ending with full-screen scrolling websites. And it’s quite hard to choose one of them for your own project because they are so popular at present moment – even though they are just some temporary trends.
All colors, effects, and other features combine together perfectly to create a complete interface that may help users to understand your idea in just one second. You need no more time to think about UX or UI matters because Google has already done it for you: there are clear guidelines in Material Design specification and they work great if you’re focusing on them! And in case you aren’t, don’t worry – everything is simple, beautiful, and understandable at the first sight.
The material design consists of these aspects:
– Material is based around the metaphor of real-world paper. It has physical surfaces, which can be attracted or repelled by other physical surfaces; these forces are visualized in the form of geometrical attraction and repulsion vectors between the elements on the screen.
– Each object’s surface has a shadow to convey depth and volume.
– Motion is used extensively in the user interface to further convey how objects interact with one another. For example, when navigating from one screen to another, objects on the new screen slide in from the side, suggesting their physical presence.
– Lighting is used to give emphasis and cast shadows to make out the form of objects on the screen. They can provide depth cues (such as rims light) or context cues (such as a light bulb). The light source could be an environmental light that illuminates all objects equally or a directional light that highlights part of the scene.
Why you should choose Material Design?
First of all, Material Design is… well, it’s new. It was first introduced to the world in 2014 and has gained a lot of attraction already. Secondly, Google is pushing for this design language through its products (e.g., Android 5). That means that sooner or later you simply have to use it anyways if you want your apps to follow some sort of UI guidelines. And lastly, the material design allows more room for creativity. Just imagine how many possibilities are at your disposal when utilizing light and shadow effects!
All in all, we think Material Design is quite the step forward for mobile app development and believe that it can bring great solutions to current problems: lack of consistency, lack of usability, and lack of simplicity. It also creates a smooth transition from mobile to web-based apps, at least according to Google’s own words.
Pros of Material Design
Material Design has a lot of advantages and here we discuss some of its key features:
1. Graceful animations
Material designs come with smooth, engaging, and flexible UI transitions and animations, making it easier for users to understand the relationship between different elements on their devices. Animations not only clarify the relationship of UI components but also help craft user’s attention at specific points. For example, movement from one screen to another or hovering over/clicking any element on your web page can be used to highlight certain elements such as images or buttons, etc.
2. Responsive layout
It offers fast-scrolling screens and quick content updates, which are important for the mobile age. The use of fast page-switching animations helps users navigate through different screens without having to wait for the screen to load. The ‘card’ layout design makes it easier to scroll vertically or horizontally, whereas elements inside each card can be pushed across the boundaries of their parent cards with ease.
3. Self-contained UI components
Material design introduces self-contained UI components that are much easier to maintain and recognize. This not only speeds up coding but also creates consistency in the user experience. These reusable UI components come loaded with preset API styles that are ready to be plugged into your website or app’s development framework. Therefore, all you need is just a little knowledge about how these API codes work, and you are good to go!
4. Adapts well to all screen sizes
You do not need to worry about how your website or app will look on any device. Material Design takes care of the responsiveness part, providing your app with a uniform look, so users can navigate through their screens easily no matter what device they are using. In addition to this, Google has recently introduced material template theming which helps developers get started by choosing from a set of pre-designed UI components and customizing them according to their needs. This method has been designed specifically for better responsive designs and faster coding.
5. Less time required to create animations
By standardizing the way different elements should be animated inside an application or webpage, material design speeds up the process of making animations. The use of common animation time scales for all elements inside the app or webpage makes it easier to create equilibrium between different components, saving a lot of development time in the process.
6. Material design is flexible
Developers can easily customize this new design language by using color, typography, and graphic elements that best suit their needs. This allows developers to choose the right material design that fits perfectly into their existing UI or UX patterns. Material Design can also be integrated with any CSS framework like Bootstrap, Foundation, etc., which means you can use Google’s official material theme along with third-party plugins like jQuery, JavaScript, etc., resulting in better-animated interfaces for your mobile apps or websites.
Cons of Material Design
Material design was introduced as a better option to be used on websites and apps rather than using flat design.
However, the material design also has some flaws which can make it less preferable to use:
1. Too many colors
Because the interface consists of many objects and different components, it becomes difficult for users to look at screens that contain too much color; especially if they’re older or color blind.
People might think that this isn’t a problem since there is an option for users to change their theme to suit what they prefer (i.e., light, dark, etc.), but sometimes people don’t like having lots of options or choices; they would want the site/app to remain simple and minimalistic, without too much hassle.
2. The animations
The objects which the material design uses move to different positions on the screen when a user performs an action such as scrolling down or clicking on an object; this can be distracting for users who aren’t interested in what’s moving around them. Some people might find that it makes their eyes hurt after a while. It may also not be suitable for people with epilepsy or other conditions that could affect how they perceive movement.
3. Too many distractions
Material design is good in some ways because it allows users to interact with content easily by performing certain actions (such as swiping left or right), but there are times when features like these become too distracting and make things difficult for users to focus on what they’re actually trying to do.
4. It has a learning curve
Many people don’t like having lots of different things or actions that they need to remember when they access a site/app because it becomes too confusing and difficult for them; they would prefer if everything is kept simple with just one task in mind.
Conclusion
Material Design is the best choice for web developers because it’s totally responsive – any element may be resized or rotated without losing its sharpness and perfect connection to other components! And that’s not all – Material Design was created with touch screen devices in mind, so you don’t have to think about the usage of your project on desktops – there are no separate interfaces for them! It makes this design great for business owners too because they are interested in the audience which uses lots of devices every day.
Author Name: Khurshid Alam
Author Bio: Khurshid Alam is the founder of Pixel Street, a web design company. He aspires to solve business problems by communicating effectively digitally. In his leisure, he reads, writes, and occasionally plays a game of table tennis.